Scientists discovered an Australian “dinosaur” moth that, if the evolutionary story is to be believed, has undergone virtually no evolution for at least forty million years. They named it Enigmatinea glatzella. The name is quite descriptive, as Enigmatinea means “enigma moth” in Latin. But why is this moth an enigma to evolutionary scientists? More… …read more Read more here: icr.org
Biologists from the U.K. conducted a 10-year-long experiment on common flour beetles to help understand why insects keep on using sexual reproduction despite its inefficiencies. Though they interpreted the results as supporting evolution, a key observation on the immutability of reproductive systems calls that into question. More… …read more Read more here: icr.org
Meet the tiny mouse that is unaffected by a scorpion’s deadly sting. …read more Read more here: creation.com
By Ken Ham Creationists and, as I pointed out during my debate with Bill Nye, TV’s “The Science Guy” last year, even some secular textbooks have highlighted the distinction between the two different kinds of science. One kind of science is observational science, which deals directly with the present. It’s directly testable, observable, and repeatable. It’s the kind of science that builds airplanes and cell phones, and put a rover on Mars. The other kind of science is historical science. Historical science deals with the past and is therefore not directly testable, observable, or repeatable. In historical science, the evidence [More]
By Nathaniel T. Jeanson The mechanism of speciation remains one of the most contested scientific questions among both evolutionists and creationists. …read more Read more here: AIG Daily
DNA can store computer information extremely densely. Even preserved in silica glass, it could not survive the evolutionary age of dinosaurs. So dinos with DNA could not be millions of years. …read more Read more here: creation.com
By Avery Foley Many scientists today have accepted the idea that some dinosaurs were covered in feathers. Is Jurassic World wrong for opting for scaly bodies? …read more Read more here: AIG Daily
By Dr. Elizabeth Mitchell Bioluminescence helps many animals hunt, hide, or reproduce, and it remains a riddle for evolutionary scientists. …read more Read more here: AIG Daily
I well remember the first time I heard Prof. Burgess give a lecture—on “Hallmarks of Design” in the natural world—at the 7th European Creationist Congress in 2000, one of the conference highlights for me. Here was a committed Christian and experienced engineer turning his design eye on the biological wonders of the natural world, and Stuart’s book of the same title had just been published.2 He has since authored books on topics as diverse as the stars and human origins. But do real scientists and real engineers treat Genesis as history? Well, regular readers of Creation will know the answer [More]
Did they really have a common ancestor? …read more Read more here: creation.com
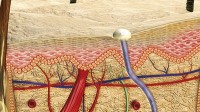
By Dr. David Menton Skin’s multilayered design provides us with the perfect combination of strength, flexibility, and durability. …read more Read more here: AIG Daily
A few years ago, scientists discovered a unique sensory organ in the jaw of a rorqual whale—the world’s largest creature. Rorqual whales, which include the blue whale and fin whale, feed by ballooning out folds of tissue that bag gobs of krill from fertile ocean waters. Some of those researchers recently described the unique bungee-cord-like nerve fibers that illustrate clever and intentional design. More… …read more Read more here: icr.org
By Dr. Jean Lightner Researchers say the “big bang” of bird evolution has been mapped, revealing the history and origin of birds, but they assume all life shares a common ancestry. …read more Read more here: AIG Daily
By Frank J. Sherwin, III Fleas are considered a nuisance. How can they be explained as a part of God’s very good creation? …read more Read more here: AIG Daily
The tuatara is a small reptile that defies evolutionary explanations. …read more Read more here: creation.com
By Dr. Elizabeth Mitchell Did millions of years in the dark evolve away cave crustaceans’ eyes and the brain to see? …read more Read more here: AIG Daily
By Yingguang Liu The molecular interaction of HIV-1 is merely cyclic fine-tuning of an existing function and illustrates the broken relationship between the virus and the host. …read more Read more here: AIG Daily
‘Atavistic tails’ and evolution: are some people born with a throwback to a tailed monkey ancestor? …read more Read more here: creation.com
The discovery of a super-complex machine has the world’s best scientific minds scrambling for answers. …read more Read more here: creation.com
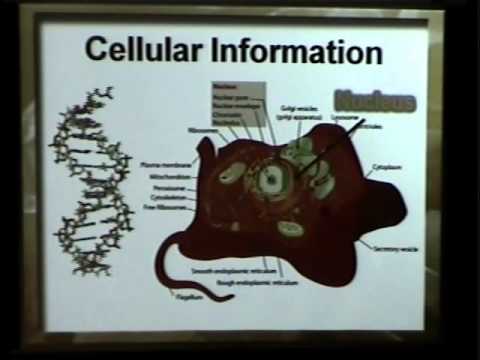
Scientists have long been baffled as to what actually tells proteins called transcription factors (TFs) where to bind in the genome to turn genes off and on. However, new research incorporating the three-dimensional shape of DNA has revealed an incredibly complex system of interacting biochemical codes. More… …read more Read more here: icr.org
By Dr. Elizabeth Mitchell Trickle-down chemistry supposedly solves the chemical conundrum concerning the origin of life, but molecules-to-man evolution remains as fictional as ever. …read more Read more here: AIG Daily
Bats are such unique creatures that their existence in the fossil record causes immense problems for evolutionary explanations of their supposed development. …read more Read more here: creation.com
“This is just one more example of protein material being preserved in fossils supposedly many millions of years old with no explanation of how this is possible. The more sensible conclusion is the fossils aren’t millions of years old.” Admin Scientists recently studying a collection of ancient shells were surprised to find not only no evidence of evolution in the specimens, but also clear evidence of protein-rich materials that normally cannot survive millions of years. According to a recent article published in the European Association of Geochemistry’s Geochemical Perspective Letters, researchers analyzed shells found along the coast of Maryland. The [More]
A complex flying machine has scientists struggling to explain how it could have come into existence. …read more Read more here: creation.com
We often hear claims that birds are similar to dinosaurs, but birds and mosasaurs? Mosasaurs were swimming reptiles. How can they be confused with birds? A recent study published in Palaeontology by Yale University’s Daniel Field and his colleagues clears up some of this confusion and in the end, illustrates a mosasaur lifecycle of marvelous design. More… …read more Read more here: icr.org
Why bother with nectar and pollen when there’s meat on the menu? …read more Read more here: creation.com
By Tom Hennigan Chameleons’ skin color can shift dramatically, and in just a few minutes their colors can revert back to the original. How do they do this? …read more Read more here: AIG Daily