Two scientists can examine the same data and reach very different conclusions. Is that proof that science is broken or simply evidence that assumptions matter? A recent paper in Science Advances claims that a researcher’s personal views can shape scientific results.1 The authors suggest this reveals a serious weakness in science itself. However, their study does not indicate that science is broken. Instead, it show... More...
Recent conventional genetic research published in Cell Genomics undeniably confirms findings that were previously reported by the Institute for Creation Research back in 2013.1 Once again, current conventional research has vindicated the prior creation exposure of evolutionarily inconvenient data present (but disregarded) in conventional databases.
One of the most popular arguments used to support the supposed... More...
Bird calls are something we often take for granted. After all, when we listen to them, we hear squawks, warbles, and chirps. Could there actually be information, something complex, that they’re transmitting? Scientists now say “yes” after studying a fun-sounding bird from New Zealand—the pukeko.1
Bird sounds are classified into calls and songs. Calls are simple and short, such as an alarm call. ... More...
Some discoveries stand out, not because they change the story of evolution, but because they show clear design from the start. That is what happened when scientists found a new crocodile-like fossil in Egypt’s Western Desert called Wadisuchus kassabi. At first it may look like another ancient reptile, but a closer look shows something more exciting—a creature built from the start for life in the water, not a half-formed s... More...
What was the pre-Flood world like thousands of years ago?1,2 With the advent of unearthing soft tissues in fossils,3 creation scientists continue to construct a picture of the world before the Flood.
Metabolomics is the study of chemical processes involving small molecules that were part of fats, proteins, amino acids, and nucleic acids. It is a field in biological research that has only occasionally been ap... More...
A galaxy with the designation MoM-z14 has recently been confirmed as the most distant galaxy ever detected.1,2 By Big Bang reckoning, we are seeing this galaxy as it was just 280 million years after the supposed Big Bang. This shocked conventional scientists, because slow, gradual, evolutionary processes should not have been able to form such a “remarkably luminous”2 galaxy in such a short time.
... More...
Hugh Ross’ latest book, Noah’s Flood Revisited: New Depths of Insight from Science and Scripture, is both dismissive of young earth creation (YEC) research and full of fabricated tales.1 Nonetheless, he begins his book by sounding fairly reasonable for the most part. In the first three chapters, he reminds readers of the literal and historical account of Noah in Genesis: it was a real event and not merely poetr... More...
The word evolution is often used imprecisely, leading the public to believe that any biological change is evolution, and, therefore, it’s a fact.1 But phenotypic variation within the same species has nothing to do with evolution.
Recently, biological research has been conducted aboard the International Space Station (ISS) by the University of Wisconsin-Madison.2 Scientists wanted to see how conditions ... More...
Research into insect eyes continues to reveal amazing structure and function. For example, although fruit flies’ eyes are attached firmly to their heads, it was discovered that their retinas can move internally to smoothly track visual motion.1
Scientists from the University of Konstanz, Germany, recently discovered how light is processed by the brain of the hummingbird hawk-moth. They uncovered the incredible ma... More...
"Be strong and of good courage, do not fear nor be afraid of them; for the LORD you God, He is the One who goes with you. He will not leave you nor forsake you." (Deuteronomy 31:6, NKJV)
ICR'... More...
Water that is nearly five times saltier than the ocean is deadly to most animals. But in Utah’s Great Salt Lake, scientists have found a tiny roundworm living in these harsh waters. The organism, called Diplolaimelloides woaabi, was recently described in the Journal of Nematology.1 Its discovery gives a clear example of how life can function at the edge of what is possible. More than adding a new species name,... More...
What if every living creature—from coral reefs and cold-water fish to mountain flowers and desert reptiles—followed the same hidden temperature rule? Scientists at Trinity College Dublin recently reported that all life seems to follow a single pattern called the universal thermal performance curve. This curve shows how living things react as temperatures rise and fall.1 The study, published in Proceedings of the Na... More...
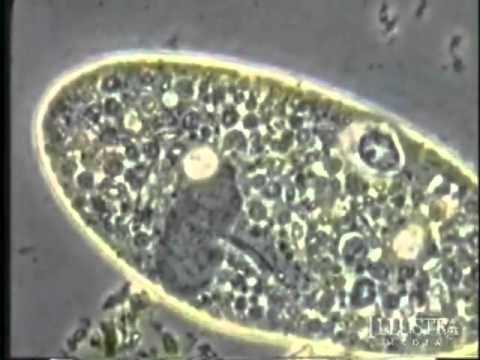
Research into God’s living creation is dynamic and always surprising. This is true whether one peers into the deepest reaches of space or dives into the unexpected in laboratory research. Indeed, the vast field of microbiology (bacteria, fungi, and archaea) has barely been touched when it comes to discovering and describing new species of organisms.
In 2011, scientists found a strange and fascinating single-celled microorga... More...
An open access 2026 PeerJ research paper claims that T. rex took 40 years to reach its full adult body size, in contrast to a much shorter previous estimate of 25 years.1–3 This study is arguably the most rigorous dinosaur growth study ever performed, and it was based on more data than any earlier T. rex analyses. Longevity studies in living animals consistently show that animals that take longer ... More...
A new discovery of 18,000 individual dinosaur tracks in the Bolivian El Molino Formation contains the highest number of theropod dinosaur tracks in the world.1 The tracks were spread over nine sites in an area encompassing nearly 1.5 football fields. Remarkably, the site also contains the highest number of dinosaur swim tracks ever reported.1
Publishing in PLoS One, the joint science team from the Uni... More...
The fascinating flying reptiles called pterosaurs are in the news again.1 In a not-so-surprising development, paleontologists have discovered a pterosaur fossil that was found to have small stones (used in the gizzard to grind food) and plant microfossils at the stomach mass.2 This indicates the pterosaur ate vegetation, lending credibility to the creation model. According to evolutionist Eric Ralls, “The researc... More...
Research by ICR geneticist Dr. Jeff Tomkins was at the center of origins news in what has been called the “No. 1 Story for 2025.”1 The prestigious journal Nature confirmed (albeit grudgingly and belatedly) that the true genome-wide DNA similarity between humans and chimpanzees is no more than 85%,2 rather than the 98%–99% similarity that has long been touted in both the technical and popular sc... More...
Imagine a machine that keeps working even when its parts change slightly or its surroundings shift. Most human-made machines would fail under that kind of stress. Living cells, however, manage this every day. Life is not weak or accidental. It shows flexibility, responding to change while keeping its basic function. A recent study in Nature Ecology & Evolution highlights this ability, showing biological systems that seem prepared... More...
by Jeffrey P. Tomkins, Ph.D., and Frank Sherwin, D.Sc. (Hon.)*
The fascinating pollination of plants has been complex from the beginning of creation. A recent article in Science magazine reported how cycads—large, palm-like seed plants—use infrared radiation as a pollination signal to beetles.1,2
The evolution-defying cycad is finely tuned to emi... More...
by Jake Hebert, Ph.D., and Frank Sherwin, D.Sc. (Hon.)*
A small portion of surface ice in Antarctica is called blue-ice areas (BIAs), and for good reason. Air bubbles were squeezed out of the ice, giving it a clear, bluish tinge. The ice is beautiful, but is it as old as evolutionists claim?
In 2025, scientists discovered supposed “6-million-year-old ice” in blue ... More...
“For I determined not to know anything among you, save Jesus Christ, and Him crucified.” (1 Corinthians 2:2)
When Paul first entered the Greek city of Corinth, he had just come from nearby Athens and his encounter with its humanistic philosophers at Mars’ Hill (Acts 17:18–18:1). Corinth, ... More...
“All thy garments smell of myrrh, and aloes, and cassia, out of the ivory palaces, whereby they have made thee glad.” (Psalm 45:8)
One of the most beautiful of the Christmas hymns (though rarely sung at Christmas) is “Out of the Ivory Palaces,” telling how the King of heaven left His heavenly home and laid aside His perfumed, royal clothing to enter &l... More...
“Therefore God also has highly exalted Him and given Him the name which is above every name, that at the name of Jesus every knee should bow, of those in heaven, and of those on earth, and of those under the earth, and that every tongue should confess that Jesus Christ is Lord, to the glory of God the Father.” (Philippians 2:9 –11)
At Christmas time, Ch... More...
What if a fossil no bigger than a grain of rice showed engineering so precise that it still puzzles scientists? That is the intrigue surrounding Salterella, a tiny cone-shaped creature recently studied by Virginia Tech researchers. Their work highlights a surprising feature—a shell made from two different minerals. They describe it as an evolutionary “experimentation” from the start of animal life.1 Yet t... More...
Evolutionary naturalism is locked into seeing the entire living world as having evolved from a single common ancestor many millions of years ago.1 If true, the fossil record should document this slow and gradual change with untold transitional forms that smoothly bridge one kind of creature to another as depicted by Darwin’s tree of life. But
Darwin’s tree illustrated a long macro... More...
A recent study published in Nature Ecology & Evolution claims that the “impossible” actually happened—not just once, but three different times.1
Impossible Ocean Barriers
The impossibilities began with the discovery of a new fossil rhinoceros species on Devon Island in the Canadian High Arctic. This smaller and thinner version of today’s African rhino was... More...