Increasingly, orphan genes defy evolution and support the Genesis account of creation. These genes are unique sets of coding sequences specific to particular creatures. This is a big problem for evolutionary ideas to explain. In a recent research report, scientists describe a new set of 1,307 orphan genes that are completely different between humans and chimpanzees. More… …read more Read more here: icr.org
Naturalistic objections to the design argument from autopoiesis fail by begging the question. …read more Read more here: creation.com
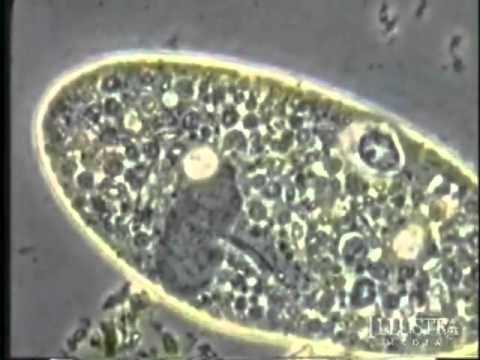
‘Autopoiesis’ (self-making) shows that all aspects of life lie beyond naturalistic explanations. …read more Read more here: creation.com
By Dr. Georgia Purdom The issues of cloning and stem cells raise many emotional and ethical concerns. How do we think biblically regarding these topics? …read more Read more here: AIG Daily
By Dr. Elizabeth Mitchell Scientists believe protein sequences from dinosaur blood vessel walls may help them map evolutionary relationships. …read more Read more here: AIG Daily
Many zoologists consider cuttlefish to be the most intelligent invertebrate species, which is quite a problem from an evolutionary perspective. Evolutionists view intelligence evolving through social interactions and long lifespans. But cuttlefish are cephalopods. They don’t have a complex social structure and live only about a year—the lifespan of a butterfly. How did cuttlefish become so bright? More… …read more Read more here: icr.org
Researchers at the University of Texas Southwestern Medical Center discovered a gene called NORAD that, unlike protein-coding genes, makes a long functional RNA that works directly in the cell’s nucleus. NORAD helps preserve the correct number of chromosomes in cells (e.g. 46 for humans). Conversely, the cellular chromosome number becomes unbalanced when the NORAD gene goes awry, a common trait in cancerous cells. Could the NORAD gene aid cancer research? More… …read more Read more here: icr.org
Incredible lens engineering in an ‘early’ creature. Trilobites, described by Stephen Jay Gould as ‘everyone’s favourite invertebrate fossil,’ are a class of marine arthropods which are often well preserved and of striking appearance.1,2 They are believed to be extinct. They are mostly between 10 and 50 mm long (3/8 to two inches) although a few species attained a length of 750 mm (2 1/2 feet). Trilobites are characterized by a ridged carapace, or shell, made of chitin, divided into three lobes which give the class its name. While most trilobites had eyes, a number had none. A common [More]
Every year scientists discover new and amazing animal designs, and 2015 was no exception. Each find brings a new reminder of the same message every generation needs to hear: “The heavens are Yours, the earth also is Yours; The world and all its fullness, You have founded them. The north and the south, You have created them.” More… …read more Read more here: icr.org
By Dr. Elizabeth Mitchell Some think acorn worms, virtually unchanged since the Cambrian explosion, represent an evolutionary link between invertebrates and humans. …read more Read more here: AIG Daily
By Frost Smith Creationist scientists Drs. Tomkins and Bergman came up with an overall DNA similarity between humans and chimps of around 81%—quite a difference! …read more Read more here: AIG Daily
‘Superbugs’ are seen by some as evidence of evolution in action but the truth is rather different. …read more Read more here: creation.com
By Todd Charles Wood Re-analysis of O’Micks’ character sets show that the lack of baraminic distance correlations is likely the result of a small taxon sample. …read more Read more here: AIG Daily
Advocates of vertical evolution think their beliefs are as factual as the earth orbiting the sun. However in 2015, science again shows something quite different. A supposed 150-million-year-old fossilized crab larva, discovered in Germany this year, surprised secular scientists because it “possesses a very modern morphology, indistinguishable from many crab larvae living today.” More… …read more Read more here: icr.org
By Frost Smith What can we do to help corals survive and why should we want to? …read more Read more here: AIG Daily
Rather than ‘evolution in action’, claims of a new weed species show that the Designer created complexity that allows for speciation. …read more Read more here: creation.com
A team of French and Canadian scientists have identified preserved embryos within the eggs of a tiny shrimp-like creature believed to have lived over 500 million years ago, raising questions about both the development of the creatures’ brooding abilities and the likelihood of such delicate materials surviving for thousands of millennia. Waptia fieldensis is a tiny, shrimp-like arthropod whose fossilized remains were first found 100 years ago in Cambrian layers of fossils in Canada. Now extinct, Waptia was a frail creature that carried the eggs of its young within its own body. Canadian researchers studying Waptia specimens recently made a [More]
Might it actually be evidence for design? …read more Read more here: creation.com
By Dr. Elizabeth Mitchell Evolutionists claim human intelligence, culture, and society evolved because an ape-like ancestor’s brain evolved the need to be shaped by the environment. …read more Read more here: AIG Daily
By Dr. Andrew Fabich ERVs are found in the same location in the genome across species, so evolutionists apply their ideas of common ancestry and say ERVs demonstrate evolution. …read more Read more here: AIG Daily
The BBC recently reported a group of tarantulas possessing a beautiful blue color that apparently has an important signaling function. Evolutionary researchers maintain this shade of cobalt evolved at least eight separate times. But what’s the evidence? More… …read more Read more here: icr.org
Designers of flying robotic drones have tried and failed to make autonomous landing systems, despite using lasers, radars, sonars and GPS technology. So how do bees do it so easily? …read more Read more here: creation.com
Evolutionists once thought that jumping genes were ‘selfish’ DNA, but Australian wallabies show they were jumping to the wrong conclusions. …read more Read more here: creation.com
Newfound “feathered dinosaurs” continue to garner fossil headlines. What’s the big deal? Peter Larson, part of a team that described an eight-foot tall supposedly feathered raptor fossil, explained its significance to the Rapid City Journal. The paper wrote, “He said this discovery is so important because this group of dinosaurs is ‘very, very closely related to birds.'” Did they find actual feathers? Does this fossil really confirm that dinosaurs evolved into birds? More… …read more Read more here: icr.org
By Dr. David Menton Perhaps more than any other fossil, Lucy is presented as “exhibit A” for evolutionists in their attempt to show that humans evolved from an ape-like ancestor. …read more Read more here: AIG Daily
Evolutionary claims of a new species of yeast simply fall flat. …read more Read more here: creation.com
Does a Y chromosome and estrogen in men make them confused about their sexual identity? …read more Read more here: creation.com