By Avery Foley Researchers have been working on Bat Bot (or B2), a robotic lightweight flier designed to mimic the incredible aerial ability of a bat. …read more Read more here: AIG Daily
Many think that Stanley Miller’s famous 1953 experiment showed that life could arise from non-living chemicals. But real chemistry shows that the chemicals Miller produced would react in the wrong way for life to form. …read more Read more here: creation.com
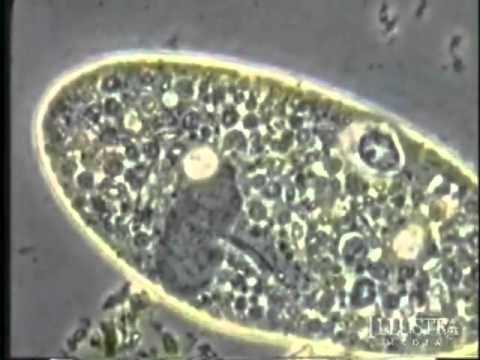
Plankton is the general name for the tiny creatures that drift with ocean tides and currents and form the basis of the ocean’s food chain. One particular group of plankton is called dinoflagellates. Recently, these were discovered to possess an amazing hunting mechanism that acts like a Gatling gun. More… …read more Read more here: icr.org
By Dr. Kevin Anderson A recent study of the salivary mucin-7 gene (MUC7) demonstrated there was genetic variation of this gene among different primate species. …read more Read more here: AIG Daily
Looking for the clearest amber on Earth? A new study shows that Dominican Republic amber is clear enough to see what’s inside. Apparently, ancient parasitic protozoans loved to live inside intact red blood cells. More… …read more Read more here: icr.org
By Tom Hennigan Forests are nurseries of health and well-being. New discoveries are showing that this doesn’t happen by accident. The trees are working together. …read more Read more here: AIG Daily
River trout have been found with amazing resistance to toxic pollutants but this turns out to be in-built. …read more Read more here: creation.com
A new study demonstrates that adult-like nervous system patterns exist throughout the early stages of human development, even in the hands and feet. These results add to the increasing evidence that aborted babies experience severe traumatic pain during all stages of pregnancy. More… …read more Read more here: icr.org
The traditional evolutionary model states that organisms evolve by random mutations. These mutations somehow provide new genetic information leading to novel traits that can be selected upon by the environment. Now, a new study shows mutations that commonly arise during cell division are not only unhelpful, but instead are highly correlated with cancer. More… …read more Read more here: icr.org
By Ken Ham One of our supporters recently sent us a photo of an exhibit at a major US metropolitan zoo. The sign at this exhibit says that dolphins were both “designed for the depths” and “perfectly adapted for life in the water.” Since apparently it’s National Dolphin Day today (April 14), I thought I’d share the photo with you. Evolutionists often try to explain evolution by claiming that the evolutionary process supposedly designed a particular creature for its environment. But naturalistic evolutionary processes are random and purposeless—they couldn’t design anything. And what about adaptation? Well, what they mean …read [More]
By John UpChurch Your eye’s complex ability to see color and motion points to the Creator. Even its limitations reveal His purposeful design. …read more Read more here: AIG Daily
18th century skeptic David Hume formulated some of the most famous arguments against design. Do they stand us under scrutiny? …read more Read more here: creation.com
Mutations cause variety in the coat colours of animals. These mutations are all ‘downhill’, in the wrong direction for mutations to make microbes-to-man evolution feasible. …read more Read more here: creation.com
By Dr. Elizabeth Mitchell Are human feet the foundational distinction between knuckle-walking apes and us? How did we learn to walk this way? …read more Read more here: AIG Daily
Were creatures designed with genomic plasticity to enable them to adapt as they reproduced and filled the earth? …read more Read more here: creation.com
This mammal with a leathery armour was once rare in Texas, but its ‘conquest’ of that state-and beyond-conveys a strong message. …read more Read more here: creation.com
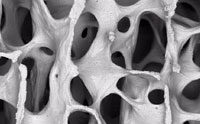
How does one build a structural material that withstands stress and fracture? The answer is to copy optimal designs from living systems because they far exceed man’s ingenuity. Recently, an improved steel was developed by copying human bones. More… …read more Read more here: icr.org
The old seafarers’ tales should not have been dismissed. Many species of squid can, and do, fly. …read more Read more here: creation.com
By Avery Foley A frog’s ability to grab and eat such a variety of food—and so quickly—is a testament to the creativity of the Designer. …read more Read more here: AIG Daily
A 15-year-long project finally bore fruit after researchers painstakingly identified a specific gene mutation that can lead to sudden heart failure in otherwise healthy-looking young people. These newly published results counter the long-standing view that mutations can somehow drive evolutionary innovation. More… …read more Read more here: icr.org
“More marvels of design that we are supposed to believe were the product of random chance processes … yeah, right.” Admin Scuba divers can explore underwater depths firsthand because of specialized equipment that was developed in just the last century. Likewise, solar-powered airplanes currently in development promise to provide fuel-free flying. These inventions open new realms for human exploration, but the arachnid and insect equivalents of their equipment have been on the planet for ages. Scuba is a stand-alone word today, but it began as the acronym for “self-contained underwater breathing apparatus,” so named because it supplies breathable air underwater. [More]
Scientists are discovering engineering details of the biological structures that enable some animals to jump exceedingly far for their sizes. Froghoppers are insects that can jump 100 times their body length, and it turns out that sheer muscular strength is not nearly sufficient to account for this feat. Read More: Insect Designed with a Spring in Its Step | The Institute for Creation Research
Sea urchins are spiny marine animals. Some of them like to hide in holes that they dig out of limestone in the ocean floor, using teeth that are ground down and yet remain sharp. What makes these teeth so special that they can drill through rock and not go blunt? Israeli scientists found remarkably precise and efficient construction when they took a close look at the sea urchins’ teeth. Using various high resolution imaging techniques, they saw tiny edges of magnesium calcite crystals exposed on the tooth surfaces. The sea urchins manufacture these crystals so that as the tooth wears [More]
When mud that encases the larva of a particular African horsefly dries out and breaks up, it does so in a way that protects the insect. …read more Read more here: creation.com
By Dr. Elizabeth Mitchell Observable science confirms preserved collagen fragments in dinosaur bone are authentic, but does not show protein can be preserved for millions of years. …read more Read more here: AIG Daily
By Dr. Elizabeth Mitchell Saccorhytus is, the authors believe, the oldest and simplest known deuterostome, the evolutionary forebear of all vertebrates and some invertebrates. …read more Read more here: AIG Daily
By Ken Ham We’ve pointed out many times that the topic of creation vs. evolution isn’t science vs. the Bible or science vs. religion. It’s one interpretation of the evidence competing with a different interpretation of the evidence. I thought I would use a new study that came out of my homeland of Australia as an example to show you how this works. Looking Through Secular Lenses Researchers are studying hairs from Australian aborigines to “help reconnect indigenous families with ancestral communities.” Here are their conclusions and interpretations based on the genetic data: “Aboriginal Australians descended from a single population [More]